VERTICAL ELECTRICAL SOUNDING (VES)
The vertical electrical sounding (VES) method is used in investigating the variation of resistivity values with respect to depth. This method is appropriate in the measurement of the depth of semi-horizontal layers of different resistivities.
The method uses the same techniques and almost the same arrangements as common resistive methods; two electrodes transmit a known current intensity to the subsurface (current electrodes) and the potential difference will be measured by two other electrodes (potential electrodes). The most common arrays applied in the VES method are Wenner, Schlumberger and dipole-dipole, these arrays will record resistivity readings at depth in proportion to the separation distance of their electrodes.
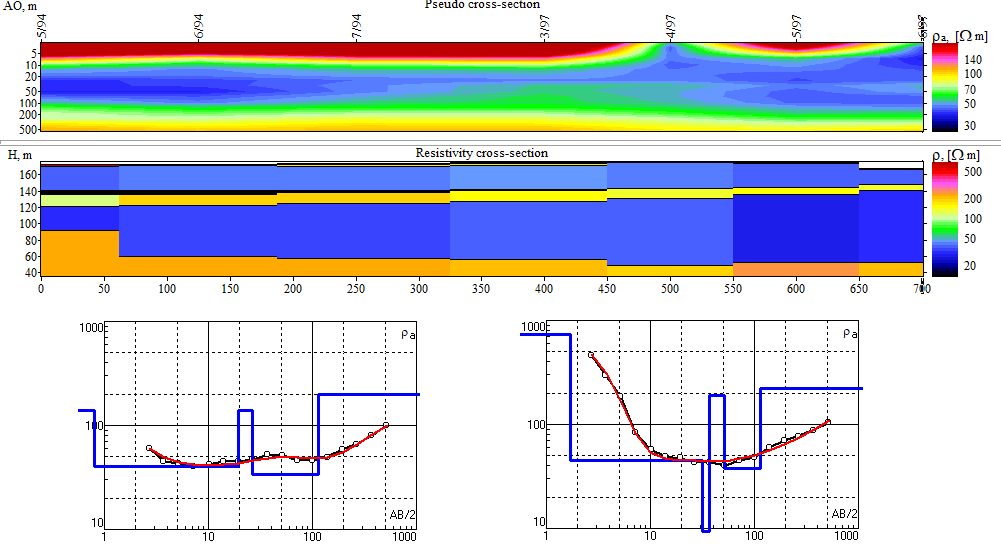
By means of analysis, 1D/2D inversion and interpretation, the method allows the determination of the overburden depth, structure and resistivity of the sedimentary layers and in some cases of the basement if it is not too deep. The method also allows the study of subsurface contamination and contaminant tracing. In addition, it is possible to study discontinuities in the mechanical properties of the rocks.
